We know Accounting profits as net income or bottom line of a company. The company arrives at this profit after deducting all costs and expenses from its total sales. This figure is shown in profit and loss account and is in accordance with GAAP. Companies calculate accounting profit either quarterly or annually or both. Costs and expenses that are used in calculation are explicit costs of running or operating a business. Costs or expenses that go into calculation of Accounting profit are - Raw materials, labor costs, such as wages, production costs, transportation costs and sales and marketing costs. Revenue sources include - sale of goods and services, rental income, interest, dividend, and more.
Today’s business owners are facing greater expectations when it comes to financial transparency and government compliance. All too often, businesses are juggling day-to-day responsibilities alongside more complex and time-consuming tasks such as finance, accounting, compliance, internal audit, and risk management.
How Accounting Profit Works?
Profit is a widely monitored financial metric that is regularly used to evaluate the health of company. Firms often publish various versions of profit in their financial statements. Some of these figures take into account all revenue and expense items, lay out in the income statement. Others are creative interpretations put together by management and their accountants. Accounting profit, also referred to as bookkeeping or financial profit, is net income earned after subtracting all dollar costs from total revenue. In effect, it shows the amount of money a firm has leave over after deducting explicit costs of running business. Costs that need to be considered include the following: labor, such as wages, Inventory needs for Production Raw materials, transportation costs, sales and marketing costs, production costs and overhead.
Accounting Profit vs. Economic Profit
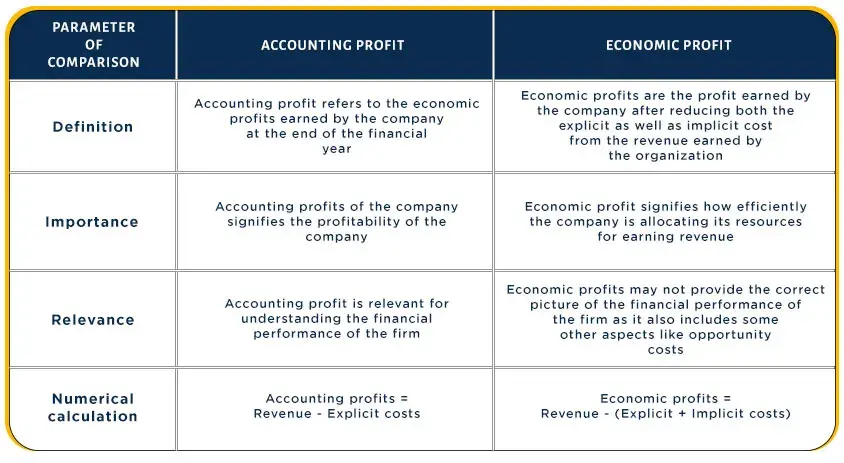
Like Accounting Profit, Economic Profit deducts Explicit Costs from Revenue. Where they differ is that Economic Profit also uses Implicit Costs; various Opportunity Costs companies incur when allocating resources elsewhere. Company - own buildings Plant and equipment Self - employment resources For example, if person invests 100 000 to start business and earns 120 000 in profit, their Accounting profit would be 20 000. Economic Profit, however, would add Implicit Costs, such as Opportunity Cost of 50 000, which represent the salary they would have earned if they kept their day job. As such, business owner would have an economic loss of 30 000. Economic Profit is more of a theoretical calculation based on alternative actions that could have been take, while Accounting Profit calculates what actually occurred and measurable results for period. Accounting Profit has many uses, including for tax declarations. Economic profit, on the other hand, is mainly just calculated to help management make decision.
Example of Accounting Profit
Example 1 Problem: Let's say that firms ' total revenue is 180 000. Using Explicit and implicit Costs from business example at bottom of section 1, what are firms Accounting and economic profits? Accounting profits equal total Revenue minus Explicit Costs. Thus, accounting profits equal 180. 000. 120,000= 60 000. From a financial point of view, assuming no changes in costs and revenue, should firm, in last example, continue to operate? The Firm reaps positive Accounting Profit of 10 000. Thus, firm has positive cash flow. However, negative economic profits indicates that if the owner had put her / his time and capital into alternative activity, he would have earned 15 000 more.
The Concept Of Accounting Profit
The concept of Accounting profit can be further simplified by comparing it with other types of profits. Three types of profits that are often confused with accounting profit are cash profit, economic profit and taxable profit. While these three types of profits are not as widely used, they are still important for businesses. Therefore, it is necessary to know the difference between these profits and Accounting profit.
Cash profit of business indicates profits it has made in monetary terms. In Accounting profit, expenses are deducted from revenues regardless of whether these expenses have been paid for or not. In other words, accounting profit also consists of accrued expenses. Cash profits, on the other hand, only consist of calculating the difference between cash inflows and outflows of business. The rule for cash profit is that if cash inflows of business exceed its inflows, it is said to have made cash profit. Cash profit is important for businesses for many reasons.
First of all, if a business keeps making accounting profits but fails to generate cash profit, it will not be able to meet its cash payment obligations on time. Therefore, business may strain its relationship with its suppliers. Furthermore, cash problems can cause business to obtain more debt to finance activities. Rising debts can also be harmful to business. Likewise, cash profits are also important because they can save business from going into liquidation. The economic profit of a business depends on its accounting profits. This is because business can calculate its economic profits by deducting its total explicit and implicit expenses from its revenues. In other words, business can calculate its economic profit by subtracting its implicit expenses from its accounting profit.
Read more: Tips To Write Small Business Financial Statements
As mentioned above, implicit expenses consist of opportunity costs of business. Businesses can calculate their opportunity cost by considering alternative uses for their resources. Implicit Expenses are subjective because businesses make judgements to calculate them. Economic profit is also an important type of profit that businesses can use to calculate their efficiency. By calculating opportunity costs of their resources, businesses can understand how efficient they are currently using those resources to generate profits.
Economic profit of business can also assist its management in making decisions regarding use of its resources. Similarly, investors and other stakeholders can use it to make decisions regarding profitability of business and whether they are better off investing elsewhere. Taxable profit is something very different as compared to cash, economic and accounting profits. Business must calculate its taxable profits under tax laws in specific jurisdictions rather than Accounting Standards. While it can deduct most of its expenses from its revenues when calculating its taxable profits, some expenses may not be allowable deductions. The Tax law of jurisdiction business is operating in will provide information regarding which expenses are deductible and which are not.
Accounting Profit: How to Calculate
Accounting Profit is final financial result identified during the reporting period based on accounting of all business operations of organization and assessment of balance sheet items under rules adopted by regulatory Accounting acts. To calculate Accounting Profit and see whether your company makes money or loses money, you will use a special formula: Total Revenues - Total Expenses = Accounting Profit / Loss. Thus, to calculate this number, you will take the following steps: find the total amount of revenue for period find the total amount of expenses for the period subtract expenses from revenue.
Example
X Corp has prepared its financial statements for year 2018 - 19. Details of revenue and profit are given below. In the above - presented case, calculated accounting profit for the year has improved in FY 18 - 19 over FY 17 - 18 by 500 33. 3% increase over PY. Revenue has increased by 10 000 25% increase over PY. It shows book profits generated by business for a particular period. It acts as a check to evaluate performance and efficiency of business. Business calls relating to further investment, profitability, market position, etc. Can be analyzed with the help of such profits.
Read More: What is the Difference Between Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable?
Advantages of Accounting Profit
What is the definition of accounting profit? This is net income report on all GAAP basis financial statements. Accountants subtract firms ' explicit costs from total revenues to calculate accounting profit. Explicit costs are costs that can be clearly identified and measure. For example, labor costs are explicit costs because they represent a specific amount pay for wages during a given period. All of the costs included in calculation are amounts actually paid except depreciation expense. This represents years ratable portion of past outlay of cash required to purchase production equipment. Thus, this also include.
Accountants do not consider implicit costs in this calculation because they have been incurred and are merely theoretical. Implicit costs are used for calculation of firms ' economic profit. Accounting profit is also known as net income for a company or bottom line. Its profit after various costs and expenses are subtracted from total revenue or total sales as stipulated by generally accepted accounting principles.
Those costs include: labor costs, such as wages. Inventory is needed for production. Raw materials. Transportation costs. Sales and marketing costs. Production costs and overhead. Accounting profit is the amount of money left over after deducting explicit costs of running a business. Explicit costs are merely specific amounts that company pay for those costs in that period - for example, wages. Typically, accounting profit or net income is reported on a quarterly and annual basis and is used to measure the financial performance of a company.
If you are looking for accountants near me for small businesses? That can do prepare your yearly taxes. Our Certified Accountants have been helping small businesses for their online accounting such as manage Bookkeeping Services, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, BAS & Financial Statements, Payroll, and Tax Return Preparation, Inventory & Cash Flow Management, etc.
We will then best match our Accounting Outsourcing Solution to your particular situation and evolve with you. Staying agile allows us to explore new ideas and gain fresh perspectives alongside your organization. Contact us today to see how we can help you thrive.


